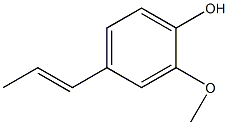
Structural formula
| Business number | 02CB |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H12O2 |
| Molecular weight | 164.20 |
| label |
2-methoxy-4-propenylphenol, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxypropenylbenzene, 2-methoxy-4-propenylphenol, 4-propenylguaiacol, 2-Methoxy-4-propenylphenol, 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxypropenylbenzene, 4-Propenylguaiacol |
Numbering system
CAS number:97-54-1
MDL number:MFCD00009285
EINECS number:202-590-7
RTECS number:SL7875000
BRN number:1909602
PubChem number:24881222
Physical property data
- Characteristics: light yellow liquid with a clove-like smell.
- Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.079~1.0851
- Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
- Melting point (ºC): -10
- Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 268
- Boiling point (ºC, KPa): Undetermined
- Refractive index (n20D): 1.575
- Flash point (ºC): 112
- Specific rotation ( º): Not determined
- Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not determined
- Vapor pressure (mmHg, 20ºC): <0.01
- Saturated vapor Pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 0.093
- Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
- Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
- Critical pressure ( KPa): Undetermined
- Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
- Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
- Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, and propylene glycol.
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: Standard Dresser test: Male skin contact, 16mg/48HREACTION SEVERITY, moderate reaction; Standard Dresser test: Rabbit skin contact, 100mg/24HREACTION SEVERITY, strong reaction; Standard Dresser test: Guinea pig skin contact, 100mg/24HREACTION SEVERITY, strong reaction; 2. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 1560mg/kg; Mouse peritoneal cavity LD50: 328mg/kg; Guinea pig oral LD50: 1410mg/kg; 3. Mutagenicity Properties: Sister chromatid exchange experiment: human lymphocytes, 250 μmol/L;
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment and it is recommended not to let it enter the environment.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 50.70
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 152.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 381.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 38.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 20.10
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 2.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 29.5
p>
7. Number of heavy atoms: 12
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 154
10. Number of isotope atoms : 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond configuration Number of centers: 1
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants.
2. Exist in oriental tobacco leaves and tobacco leaves.
3. Exist in nutmeg oil, ylang-ylang oil, etc.
4. There are two isomers, cis and trans, which have allergic effects at high concentrations. The dosage in consumer products that do not come into contact with the skin should not exceed 0.5%.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. Keep container sealed and strictly prohibited from contact with air. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the isomerization of eugenol by heating in potassium hydroxide solution. Treat eugenol or eugenol-rich essential oils with a potassium hydroxide solution to convert it into a salt. It is then heated to isomerize. After cooling, use dilute sulfuric acid to decompose the alkali metal salt, free isoeugenol, wash with water, dry, and distill under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product. Isoeugenol is found naturally in ylang ylang oil and nutmeg oil. In addition to the preparation method of eugenol isomerization, it is also prepared industrially by the synthesis method of safrole or isosafrole.
2. Heat the amyl alcohol solution of eugenol and potassium hydroxide to 200-230°C, then pour it into water, acidify it with inorganic acid, and distill the precipitated oil layer to obtain the fine product.
3. Tobacco: OR, 26; synthesis: obtained by heating eugenol and potassium solution.
Purpose
It is more elegant than eugenol for blending. It is often used as the main agent of carnation essence. It is also widely used in various other floral essences. It is very stable as a fragrance for cosmetics and soaps. It is also used as a food flavoring for apples, grapes, plums, apricots, raspberries or walnuts. It also has applications in dental medicine. In industry, vanillin is generally produced by oxidation of isoeugenol.
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/2-4.jpg
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44286
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1053
extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/9727-substitutes-catalyst-9726/
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/995
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40020
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39757
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/45-1.jpg
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/45227
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/jeffcat-td-20-catalyst-cas107-16-9-huntsman/

















Comments